A Clear and Practical Guide:How Does an Electromagnetic Buzzer Work?
1.Introduction
2.What Is the Electromagnetic Buzzer
3.Working Principle of Electromagnetic Buzzer
4.Capable Features of Electromagnetic Buzzers
5.Electromagnetic Buzzers Applications
6.How to Select the Right Electromagnetic Buzzer
7.Conclusion
Introduction
Electromagnetic buzzers are popular acoustic components that are used across a wide range of applications in order to transform electrical energy into sound. They are used in consumer electronics, household appliances, automotive systems and industrial devices as well as for numerous low-power alert systems. Because they are very cost effective, easy to drive and reliable at low voltages, electromagnetic buzzers are one of the most popular sound output devices available in modern electronics. The following blog will introduce the working principles of electromagnetic buzzer, how does electromagnetic buzzer work, main features of the electromagnetic buzzer, typical application and how to choose the right buzzer for you.
What Is the Electromagnetic Buzzer
An electromagnetic buzzer is an audio device which produces sound by using the vibration of a meta diaphragm from an electro magnetic coil. When the current is passed through the coil, a magnetic field is created. This field attracts and lets go a thin metal plate (often known as diaphragm) that vibrates at an audible frequency. The vibration causes sound waves to be produced which the human ear can hear.
Electromagnetic buzzers normally works in the frequency range of 1kHz-3kHz which is the most sensitive range of human hearing. This enables even small buzzers to be used to create loud sounds with very low power usage. They are typically constructed in small diameter casings such as 12 mm, 15 mm, or 27 mm diameter casings and are thus suitable for small devices.
There are two types of electromagnetic buzzer: Active electromagnetic buzzers and Passive electromagnetic buzzers.
Active electromagnetic buzzers: Bulit in driving circuit, They generate sound when they are driven with DC voltage.
Passive electromagnetic buzzers : With an external audio signal or square wave in order to have sound.
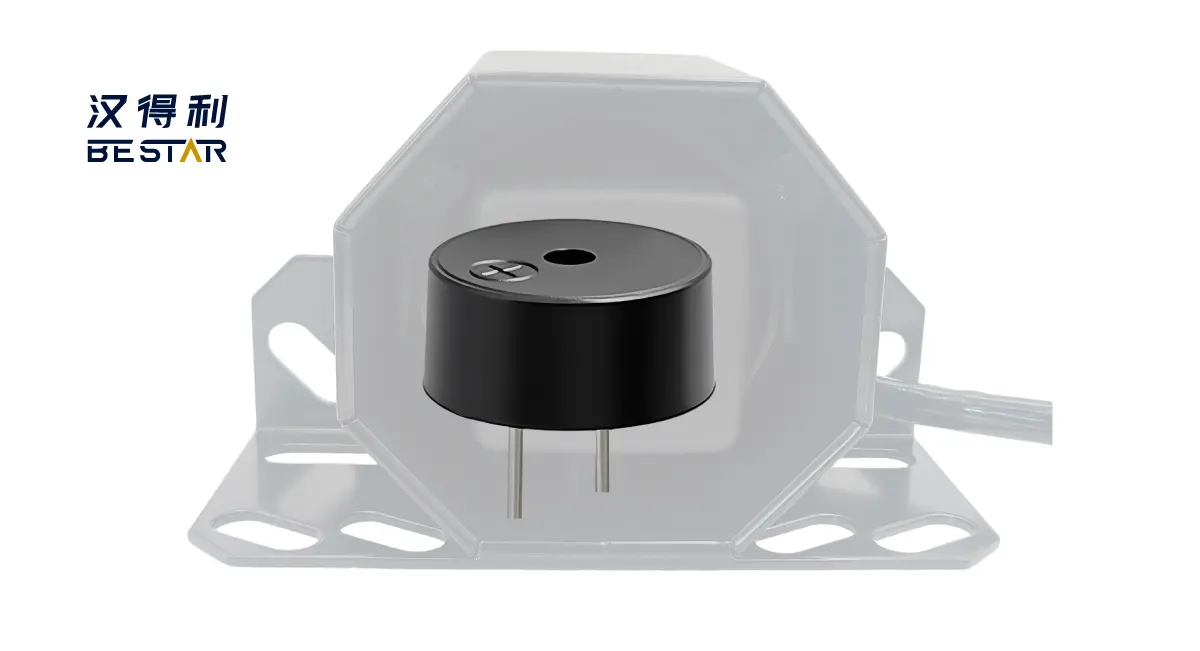

Working Principle of Electromagnetic Buzzer
The working principle of an electromagnetic buzzer is simple and high effective. It is dependent on three key factors:
Electromagnetic coil, iron core or magnetic pole and metal diaphragm. We will explain how electromagnetic buzzer sound step by step:
Step 1: Current passed through the coil. When voltage is applied there is current that flows through the coil. The coil then generates a magnetic field using the principle of electromagnetism.
Step 2: Magnetic field has an attraction for the diaphragm. The magnetic field is attracting the ferromagnetic diaphragm to the core. As the diaphragm moves it also bends slightly.
Step 3: The diaphragm returns to the original position. When the current is decreased or taken away the magnetic field collapses. The diaphragm which has natural elasticity springs back to its original position.
Step 4: Such continued repetition of vibration becomes sound. If the coil receives an alternating signal, such as a square-wave signal at 2-3 kHz, the diaphragm vibrates back and forth very quickly. These vibrations cause the pressure of the air to be pushed and creates audible sound waves.
Active&Passive Electromagnetic Buzzer Operating
Active Electromagnetic Buzzers have an built-in oscillation circuit when fed with DC voltage, the circuit produces a square wave form automatically, which is used for driving the diaphragm.
Passive Electromagnetic Buzzers take sound signals from outside, thus enabling users to vary their frequency, melody, tone patterns and loudness.
Capable Features of Electromagnetic Buzzers
Electromagnetic buzzers come with a few advantages which make them great for low voltage and cost-sensitive situations:
1. Low driving voltage
Many buzzers operate using 3 V, 5 V or 12 V that is suitable for battery powered and microcontroller based systems. This is one reason why they appear common in appliances in homes and consumer electronics.
2. Simple driver requirement
Active Buzzers only need a simple DC supply input. Passive buzzers can be driven directly by PWM ports of microcontrollers.
3. Clear and sharp sound output
The diaphragm vibration frequency is resonant frequency and hence sound output is very high but concentrate in the narrow frequency band. This helps it to be ideal for alarms and reminders.
4. Compact and light weight structure
Most electromagnetic buzzer weighs few grams. They can be able to fit in handheld devices, smart wearables, and small sensor systems.
5. Less cost and available
Compared to piezoelectric buzzers, electromagnetic buzzers typically are cheaper. This means that designers can use them in large scale production.
6. Compressible sound from frequency control
For passive buzzers, when changing input frequency directly will influence the sound tone of the buzzers. This is useful for beeping sequences or other unique sound patterns for devices that require them.
Electromagnetic Buzzers Applications
Electromagnetic buzzers are used in many industries due to their stable performances and low cost. General applications of this include:
Appliances found in the household: microwave ovens, washing machines, refrigerators.
Consumer electronics: Timer, Toys, GPUs, game controllers.
Automotive: wear seat-belts remind in dashboard.
Security and safety goods: Smoke detectors, door alarms, theft against alarm.
Medical devices: Infusion pumps, portable testing equipment.
Industrial controls: Panel chart, machine alarms.
Their loud and sharp sound makes them effective to be used for notifications where quick mutual reaction by humans is needed.
How to Select the Right Electromagnetic Buzzer
Selecting the right buzzer is relevant to achieve the expected loudness, quality and power efficiency. Below are some factors that should be considered.
1. Voltage and current
Check and see the type of voltage your system will provide, such as 3V, 5V or 12V. Also consider the current consumption especially when you are considering battery powered designs.
2. Active & passive buzzer
Choose active if you would like plug and play sound with no signal generation.
Choose passive if you are concerned with the frequency, melody or patterns.
3. Resonant frequency
Most electromagnetic buzzers are placed at the frequency range of 2 kHz-4 kHz. If you exist a particular tone, used a buzzer designed in order around one such resonance.
4. Sound pressure level (SPL)
If the application requires loud alerts, then choose a buzzer with 80-90dB SPL @10cm. For quiet environments, reductions of lower levels of SPL may be sufficient.
5. Size and mounting style
Common options include:
Through hole buzzers-appliances, industrial equipment
Surface mount (SMD) buzzers-compact electronics
6. Reliability and lifetime
Check manufacturer specifications such as operating lifetime, temperature range and shock and vibration resistance.
7. Power consumption
Reduced power consumption is critical to battery devices.
Conclusion
When choosing a electromagnetic buzzer, consider aspects such as voltage, sound pressure level, size, mounting type and whether you need active or passive design. By knowing the principle of operation and technical properties it is rather easy for engineers and product designers to select the right electromagnetic buzzer and effectively integrate it into their systems. If you want to know more about electromagnetic buzzer, you can contact us right now.