Getting Started with an Ultrasonic Sensor: Definition,Principles & Applications
1.Definition of Ultrasonic Sensor
2.Working Principle of Ultrasonic Sensor
3.Advantages of Ultrasonic Sensors
4.Applications of Ultrasonic Sensors
5.Conclusion
Definition of Ultrasonic Sensor
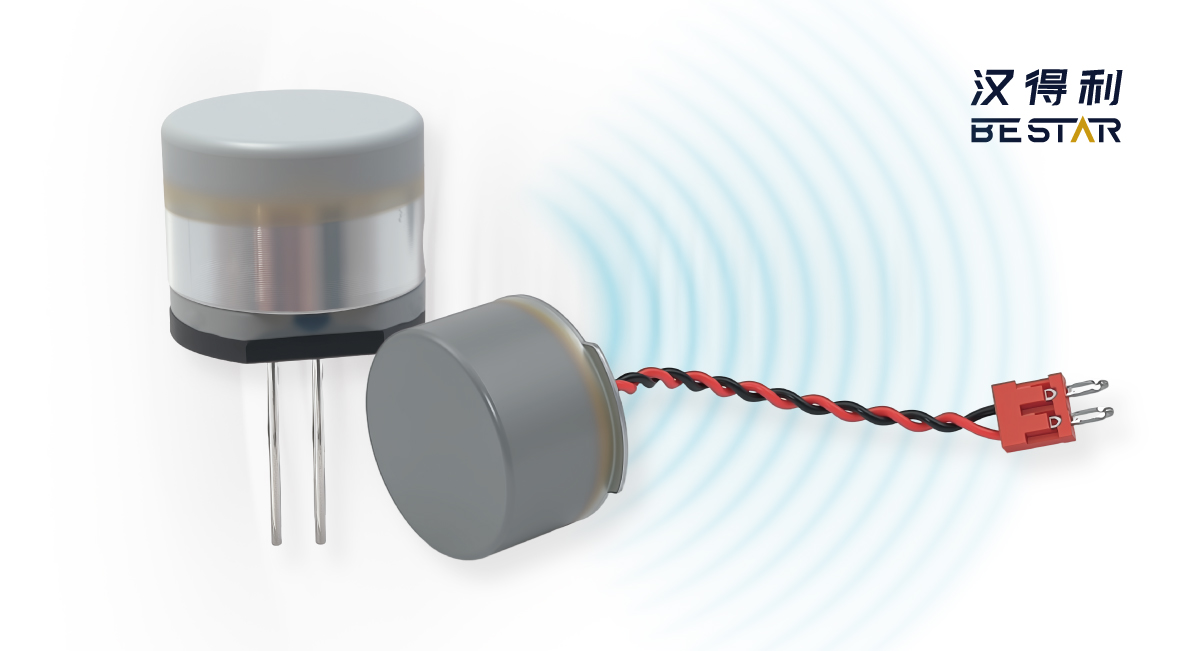
An Ultrasonic Sensor can measure distances by sending out high electrode frequency sound vibrations or high frequency waves (usually between 20 kHz and 200 kHz) and waiting for the echoes. Ultrasonic Sensors can perform the measurement with the travel-time of an echo from the object and determines the distance to that object. The sensor is able to detect objects, measure distances and track movement in conditions where light-based sensors are not suitable.
Unlike optical sensors which are based on the principle and propagation of light, ultrasonic sensors are based on the principle of sound. This allows them to work in an environment that is dusty, smoky or in poor light. They are also able to detect transparent or shiny surfaces like glass, metal or liquid accurately and consistently. They are widely used in industrial automation, automotive electronics and medical instruments.
Working Principle of Ultrasonic Sensor
The principle of ultrasonic sensor is the time-of-flight (TOF) principle. An ultrasonic sensor requires two parts, both a transmitter and a receiver. Ultrasonic transmitter sends out ultrasonic waves firstly, when these waves encounter something, they are reflected back and go into a receiver. Higher accuracy and target targets (these methods rely on frequency modulation or pulse-echo detection methods) some advanced models. Depending on the model and application, detection range can vary from a few centimeters to 10m and more. The output can be analog, digital or serial which makes the integration into electronic systems simple.
Advantages of Ultrasonic Sensors
-Non-contact Detection
Ultrasonic sensors measure distance without touching, which is especially useful for applications involving fragile, hot or dangerous materials.
-Suitable for Various Materials
They can detect almost any surface, such as solid, liquid or powder.
-Stable Operation in Harsh Environments
Ultrasonic sensors perform reliably in outdoor and industrial environments unlike optical sensor.
-High Accuracy and Fast Response
They provide precise distance measurements with typical accuracy up to ±1%. The response time can be as short as a few milliseconds, enabling real-time feedback in automated systems.
-Cost-effectiveness and Durability
Ultrasonic sensors have a simple structure, long lifespan and low maintenance requirements.
Applications of Ultrasonic Sensors
Ultrasonic sensors play an important role across multiple industries, including automotive electronics, industrial control and medical technology.
-Automotive Electronics
Ultrasonic sensors are widely used for parking assistance, blind spot monitoring and collision avoidance. They help detect obstacles around the vehicle and provide audio or visual alerts to the driver.
-Industrial Automation and Control
Ultrasonic sensors perform well in distance measurement, level detection and object counting. For example, they monitor liquid levels in tanks or silos, detect the position of moving parts on assembly lines and ensure components are correctly placed during manufacturing.
They are particularly useful for materials that are difficult to measure optically, such as grains, powders or opaque fluids.
In robotics, ultrasonic sensors provide support in collision avoidance and navigation. Many factory robots can ues them to maintain safe distances from surrounding objects or people, ensuring smooth and efficient operations.
-Medical and Healthcare Applications
Ultrasonic sensor is suitable for distance measurement, fluid monitoring and medical imaging. For instance, ultrasonic sensors in infusion pumps can detect air bubbles or ensure accurate fluid flow rates.
Conclusion
Ultrasonic sensors are general-purpose, dependable pieces of hardware that detect distance by making use of excessive frequency sound waves. They offer non contact detection and are also able to handle extreme environments and provide precise readings that make them valuable in a wide range of industries.
In the automotive field, for instance, they make life safer on the roads with parking assistance, collision prevention and autonomous navigation. In industrial automation, they adapt production efficiency and allow exact control of manufacturing and processes monitoring. In the system, they are applied in medical technology to any less invasive diagnostics or monitoring of patients.
As technology is ever advancing, ultrasonic sensors will have an even greater use in smart vehicles, Industry systems, and healthcare innovations. As signal processing and microfabrication continues to improve, these sensors are only getting smaller, faster and smarter, so they will continue to be a fundamental sensing solution in the future of automation and intelligent design.
Looking for the suitable Ultrasonic Sensor solutions? Contact our team of engineers right now for advice and a quote.