Microfluidic Cooling: A Next-Generation Solution for Heat Management
1.Definition of Microfluidic Cooling
2.Technology Behind Microfluidic Cooling
3.Microfluidic Cooling Applications.
4.Conclusion
Definition of Microfluidic Cooling
Microfluidic cooling is an innovative thermal-control system. It pumps little holes to circulate liquid which takes away heat in electronic machines. The channels tend to be narrower in diameter (few hundred micrometers). Flow of coolant is direct over hot parts, such as, chips, power modules.
Since liquid has a stronger ability to absorb heat as compared to air, microfluidic cooling can be used to produce high heat-transfer rates in a mini-environment. It is becoming a popular technique to maintain temperature in high-power, high density systems in which conventional air cooling no longer proves adequate.
Technology Behind Microfluidic Cooling
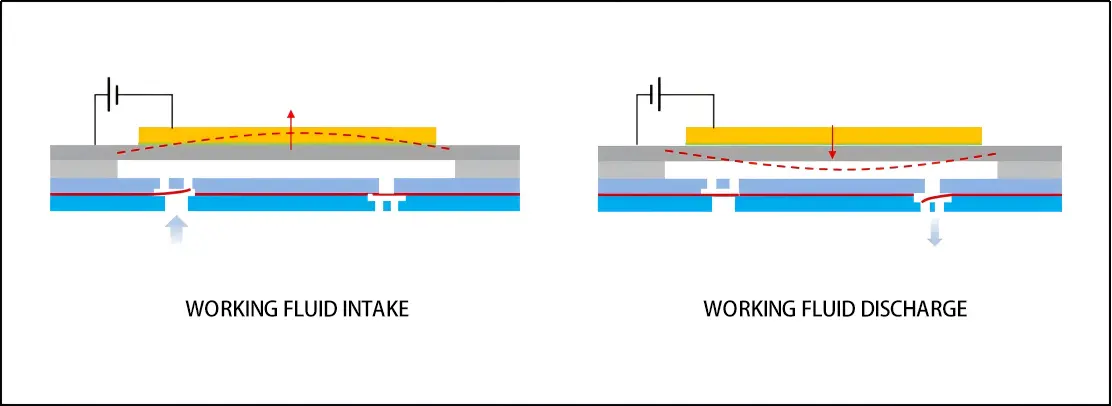
Microfluidic cooling is based on miniature channels which a liquid passes through. These microchannels are typically constructed using silicon, copper or polymer. The coolant (water, dielectric fluids or nanofluids) flows through the channels and takes the heat off-site. The microfluidic cooling system usually has a micro-pump to force the fluid and a heat exchanger to discharge the heat that has been collected. Microfluidic cooling may be set to the single-phase flow, in which the liquid remains in the same state, or a two-phase flow (where the coolant is evaporated) and the coolant is able to remove even more heat.
The format is small, and the stream may be directed accurately, making this method the best choice in the local or spot cooling. With it the temperature disparities are minimized and reliability is maximized.
Microfluidic Cooling Applications
The subject of cooling through microfluidics is common in electronics today. Microfluidic Cooling is particularly useful in high performance computing and data centers, as well as AI processors, where dense power density generates a lot of heat.
It is expanding in the automotive electronics field, the LED systems as well as the medical devices. Small size and energy savings are also essential in these aspects. Also, microfluidic lab-on-a-chip systems share the same cooling principles to maintain temperature sensitive biochemical reactions.
Conclusion
The development of microfluidic cooling is one of the key improvements in effective heat management. It involves the employment of small and accurately manufactured channels and limited stream of liquids to make high-powered electronics secure even when they are heavily loaded with heat. Microfluidic systems are more efficient at cooled sample removal time, smaller in size, and lower energy consumption than air or normal liquid cooling. With the continued reduction in the size of electronic devices and their increasing power output and influence, thermal design in future will require such cooling solutions in the coming generations in order to design AI, 5G, and other high-performance solutions.
Looking for the suitable microfluidic active cooling solutions? Contact our team of engineers right now for advice and a quote.